Introduction
Lipedema is a chronic fat distribution disorder that primarily affects women and is often misunderstood or misdiagnosed. Characterized by a symmetrical buildup of fatty tissue—most commonly in the legs and sometimes the arms—it typically spares the hands and feet, which helps differentiate it from other conditions such as lymphoedema or general obesity. Early recognition is crucial to avoid complications and ensure appropriate management.

What Is Lipedema?
Lipedema is not simply excess weight. It is a disorder of fat tissue that leads to painful, disproportionate fat accumulation. This fat is resistant to diet and exercise and with patients experiencing easy bruising.
While the exact cause is unknown, lipedema has a strong hormonal and genetic component. It frequently appears or worsens during hormonal shifts such as puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, and tends to run in families.
How Lipoedema Differs from Obesity and Lymphoedema
- Lipoedema vs Obesity: Lipoedema fat is painful, bruises easily, and is disproportionate. Weight loss through diet and exercise rarely improves the affected areas.
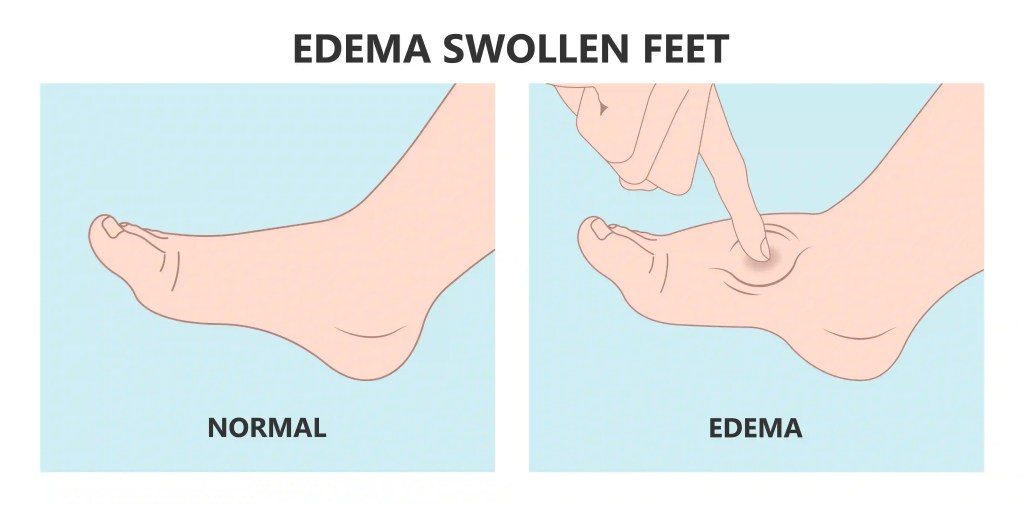
- Lipoedema vs Lymphoedema: Lipedema spares the hands and feet, while lymphoedema often involves swelling of the extremities. In later stages, however, lipoedema can lead to lipo-lymphedema, where lymphatic flow is impaired, resulting in swelling of the feet and ankles.
Associated Vascular Complications
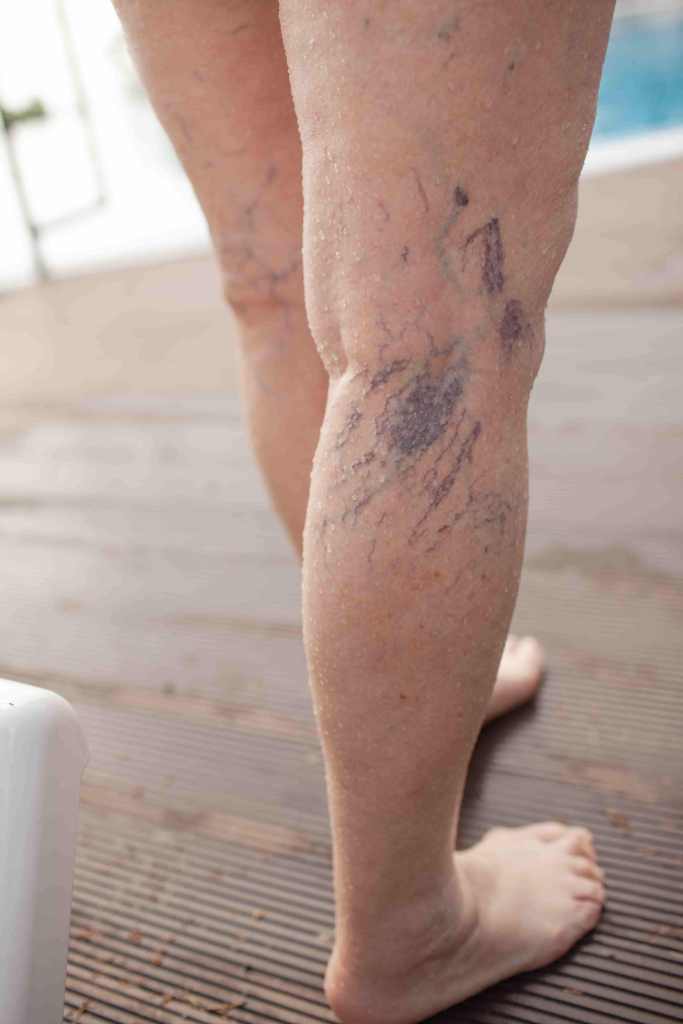
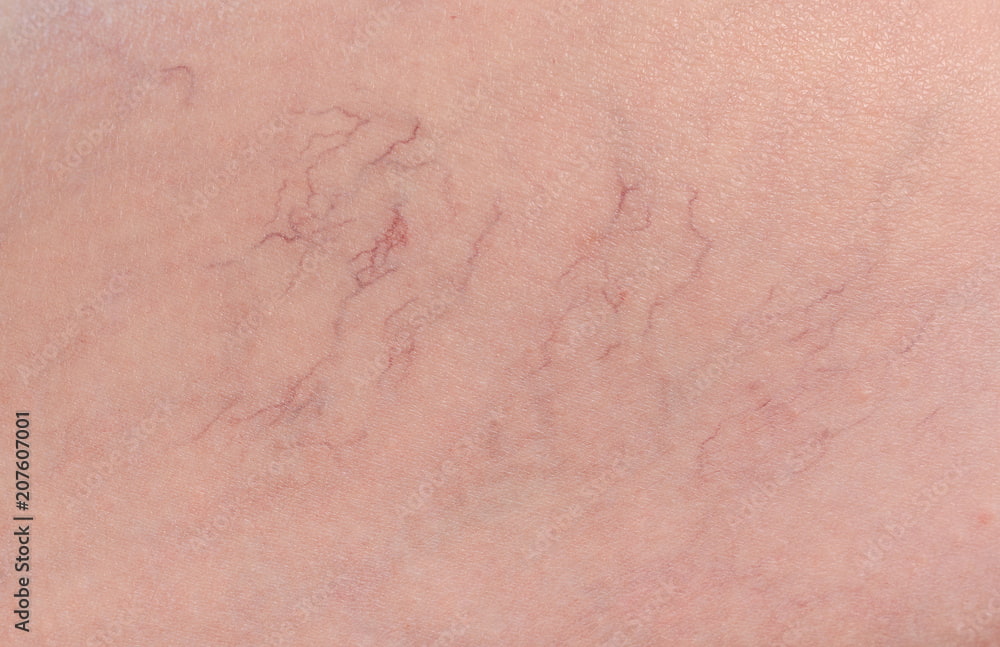
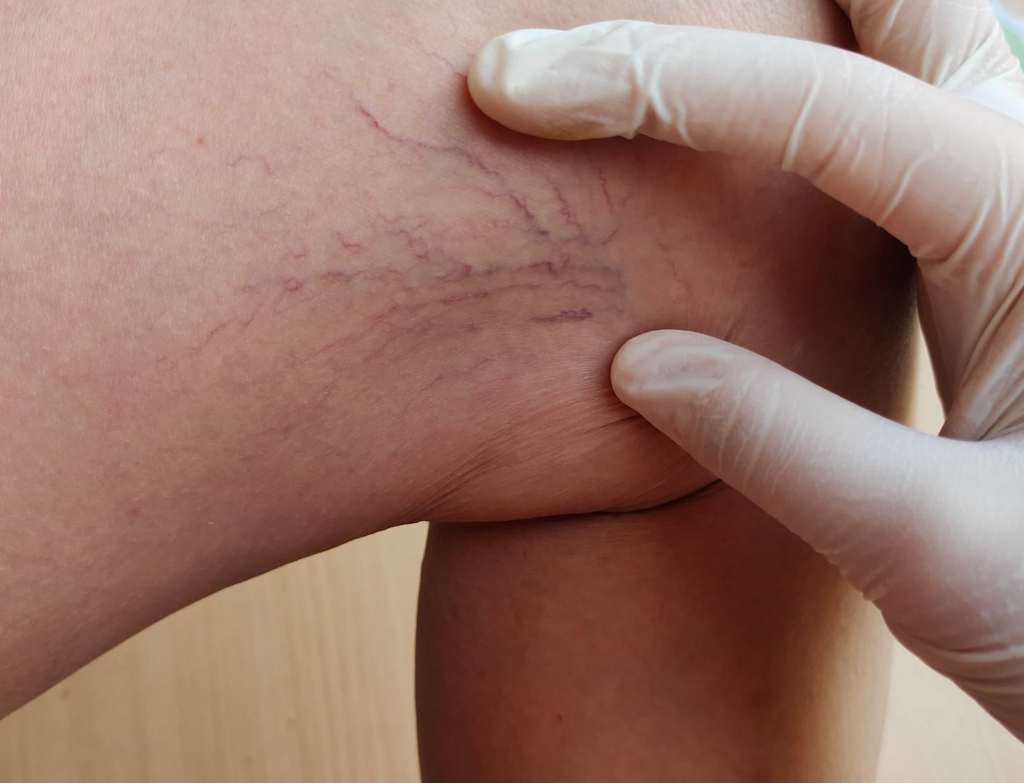
As lipoedema progresses, the excessive fat can compromise venous return and lead to chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). Patients may develop:
- Leg heaviness
- Swelling
- Varicose veins
- Skin changes such as discoloration and thickening
A Doppler ultrasound is typically performed to evaluate for venous reflux and differentiate from primary venous disorders.
Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis involves:
- Clinical history and physical examination
- Venous Doppler ultrasound to exclude reflux
- Lymphoscintigraphy (in selected cases) to assess lymphatic drainage
Due to overlapping symptoms with other conditions, many cases are delayed or misdiagnosed.
Treatment Options in Dubai
Conservative Treatment:
- Compression garments to support circulation and manage swelling
- Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD)
- Low-impact exercise such as swimming, walking, or cycling
- Skin care and prevention of infections
- Nutritional counseling to maintain a healthy weight and reduce inflammation
Advanced Treatment:
In selected cases, liposuction using tumescent or water-assisted techniques can offer long-term relief by removing diseased fat tissue. This may lead to improvements in:
- Pain
- Mobility
- Quality of life
When to See a Specialist
If you notice persistent, painful fat accumulation in your legs or arms that doesn’t improve with weight loss—and especially if your hands and feet remain unaffected—it’s time to consult a vascular or lymphatic specialist.
Patients have access to a number of vein treatment options in Dubai for the treatment of venous insufficiency if it is present alongside lymphedema.
📍 Book your consultation in Dubai for an accurate assessment.
Trusted Source
🔗 Mayo Clinic – Lipoedema Overview
Check our vein FAQ on lipidema for further information on the difference between leg edema and lipidema.
FAQs
Q1: Is lipedema the same as obesity?
No. Lipedema involves abnormal fat that doesn’t respond to traditional weight loss and is often painful.
Q2: Can lipedema cause varicose veins?
Yes. Patients with Lipidema can have venous insufficiency and varicose veins
Q3: Is liposuction a cure for lipedema?
Liposuction can significantly improve symptoms but is not a cure. It should be combined with conservative measures for best results.





You must be logged in to post a comment.